IO
Exceptions
- The
Errorclass indicates serious problems, that a reasonable application shouldn't try to catch or recover from - There are two types of Exceptions, those that subclass from
RuntimeException, and those that don't
Checked Exception
A checked exception represents an anticipated or common problem, that might occur
We have two ways to handle checked exceptions:
- We can wrap the statement that throws a checked exception, in a
trycatchblock, and then handle the situation in the catch block - We can change the method signature, declaring a
throwsclause, and specifying this exception type
LBYL and EAFP
- "Look Before You Leap" or LBYL - style of coding involves checking for errors, before you perform an operation
- EAFP stands for, "Easier to Ask Forgiveness than Permission" assumes an operation will usually succeed, and then handles any errors that occur, if they do occur
| Feature | LBYL | EAFP |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Check for errors before performing an operation | Assume that the operation will succeed and handle any errors that occur |
| Advantages | Can be more efficient if errors are rare | Can be more concise and easier to read |
| Disadvantages | Can be more verbose if errors are common | Can be more difficult to debug if errors are unexpected |
Unchecked Exception
- A checked exception means it's NOT an unchecked exception :)
- An Unchecked Exception is an instance of a RuntimeException, or one if its subclasses
finally
The original purpose for the finally clause, was to have a single block of code to perform cleanup operations
- Is used in conjunction with a
trystatement - A traditional try statement requires either a
catchor afinallyclause, or can include both - It is always declared after the catch block if one is declared
- Its code is always executed, regardless of what happens in the try or catch blocks
- Does not have access to either the try or catch block's local variables
Disadvantages:
- It can be difficult to read and understand code, that uses this clause
- It can be used to hide errors, which can make debugging more difficult
- If We execute code that's not related to clean up tasks, this will make it harder to maintain our code
Try-with-resources
| try-with-resources examples | traditional try clause |
|---|---|
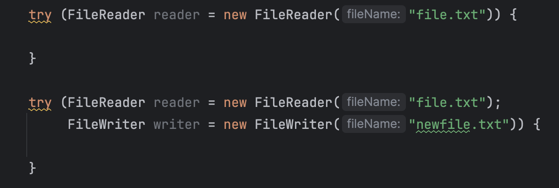 | 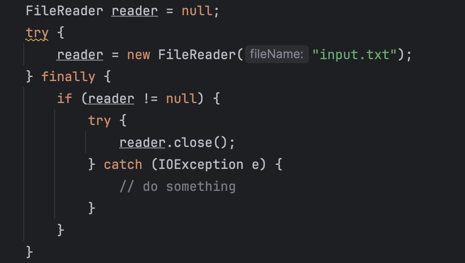 |
- The try-with-resources takes a colon delimited list of resource variables
- The resources in this list must implement the
AutoCloseableor theCloseableinterface - The try-with-resources statement can be used without a
fnallyblock, because all resources are automatically closed when this type of try block completes, or if it gets an exception