Security
- Implemented using Servlet filters in the background
- Two methods of securing an app: declarative and programmatic
Declarative Security
- Define application’s security constraints in configuration
- All Java config: @Configuration
- Provides separation of concerns between application code and security
Programmatic Security
- Spring Security provides an API for custom application coding
- Provides greater customization for specific app requirements
Spring Security with Servlet Filters
- Servlet Filters are used to pre-process / post-process web requests
- Servlet Filters can route web requests based on security logic
- Spring provides a bulk of security functionality with servlet filters
Security Concepts
Authentication
- Check user id and password with credentials stored in app / db
Authorization
- Check to see if user has an authorized role
Enabling Spring Security
- Will automatically secure all endpoints
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
- Override default username / password
spring.security.user.name=scott
spring.security.user.password=test123
Configuring Basic Security
- Create configuration
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfiguration {
// ...
}
- We can create in-memory users
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfiguration {
@Bean
public InMemoryUserDetailsManager userDetailsManager() {
UserDetails john = User.builder()
.username("john")
.password("{noop}test123")
.roles("EMPLOYEE")
.build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(john, mary, susan);
}
}
Password data encryption ids:
-
{noop}- plain text :( -
{bcrypt} -
We can restrict access based on role
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests(configurer ->
configurer
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/api/employees").hasRole("EMPLOYEE")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/api/employees/**").hasRole("EMPLOYEE")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/api/employees").hasRole("MANAGER")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.PUT, "/api/employees").hasRole("MANAGER")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.DELETE, "/api/employees/**").hasRole("ADMIN"));
// use HTTP Basic authentication
http.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults());
return http.build();
}
Read / write user account from / info database
- Following Spring Security’s predefined table schemas
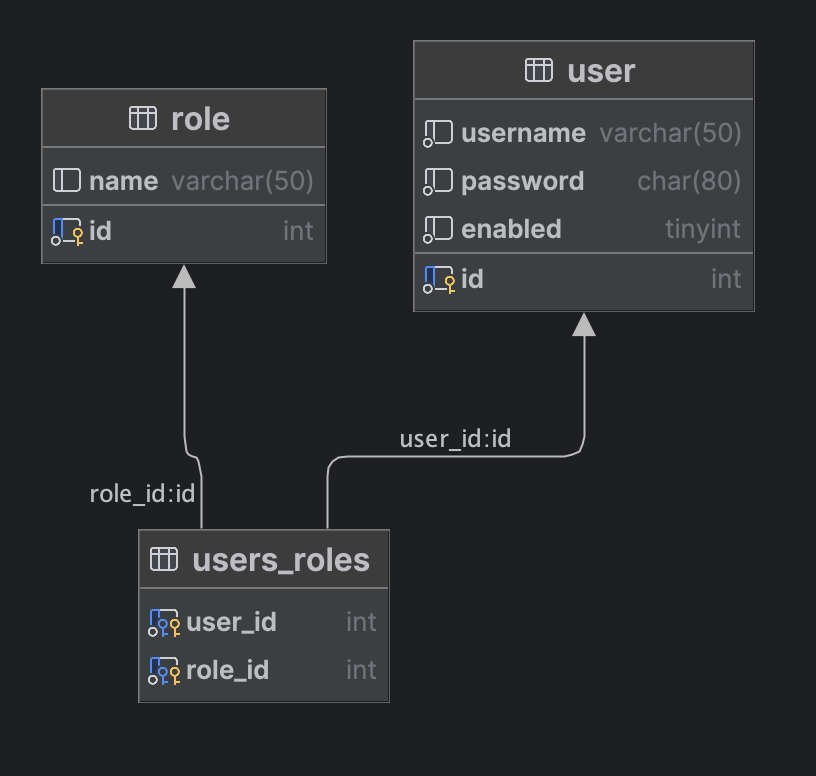
caution
Password column must be at least 68 chars wide
{bcrypt}- 8 chars- encodedPassword - 60 chars
- Basic custom setup example
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfiguration {
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
public DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider(UserService userService) {
DaoAuthenticationProvider auth = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
auth.setUserDetailsService(userService);
auth.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
return auth;
}
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests(configurer ->
configurer
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/api/employees").hasRole("EMPLOYEE")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/api/employees/**").hasRole("EMPLOYEE")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/api/employees").hasRole("MANAGER")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.PUT, "/api/employees").hasRole("MANAGER")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.DELETE, "/api/employees/**").hasRole("ADMIN"));
http.httpBasic();
http.csrf().disable();
return http.build();
}
}